Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changer in various fields in the age of rapid technological advancements. One area where AI is making significant waves is biomedicine, with the potential to revolutionize healthcare as we know it. AI is rapidly reshaping the biomedical landscape, offering unprecedented advancements in disease diagnosis, drug discovery, personalized medicine, and more. In this article, I will explain how AI transforms disease diagnosis, drug discovery, personalized medicine, medical imaging, and the ethical considerations surrounding its uses in Biomedicine.
Discover the transformative power of AI in biomedicine. Explore how Artificial Intelligence is reshaping disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalized medicine. Dive into the future of healthcare with AI-driven innovations.
Opportunities of AI In Biomedicine: Revolutionizing Healthcare with Artificial Intelligence
1. Advanced Disease Diagnosis using AI
Imagine a world where diseases can be detected accurately and quickly, even in their early stages. AI is making this a reality. With its ability to analyze large medical datasets and identify useful patterns, AI-powered advanced algorithms are becoming indispensable in disease diagnosis. Conditions like cancer, diabetes, and rare diseases are being diagnosed with unprecedented accuracy, leading to better treatment outcomes. Also, it can analyze complex medical data, including imaging and electronic health records. For instance, AI systems have demonstrated proficiency in detecting conditions like lung cancer and diabetic retinopathy through imaging analysis, often matching or surpassing human experts in accuracy.
2. Drug Discovery and Development
In biomedicine, the process of discovering and developing new drugs is a complex and time-consuming endeavor. AI is changing the game by sifting through mountains of data to predict potential drug candidates. The integration of AI in drug discovery is expediting the identification of potential therapeutic compounds. Companies like Insilico Medicine have utilized AI to identify drug candidates for diseases such as fibrosis in a fraction of the traditional timeframe. AI also aids in predicting drug efficacy and safety profiles, streamlining the development process
3. Personalized Medicine using AI
Personalized medicine is another important area in biomedicine, It enables the customized treatment plan based on the individual patient’s genetic profiles, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Because one size does not fit all when it comes to healthcare. This approach ensures that treatments are more effective and have fewer side effects, marking a shift towards truly patient-centric care. Platforms like Tempus analyze clinical and molecular data to tailor cancer treatments, enhancing efficacy and minimizing adverse effects
4. AI in Medical Imaging
In recent days, the advanced machine learning algorithms’ prowess extends to interpreting medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. By assisting radiologists in their assessments, AI improves diagnostic accuracy and reduces the risk of human error. This is especially critical in time-sensitive situations where early and precise diagnosis is paramount.
5. AI in Surgical Procedures
In Biomedicine, Surgery is a more crucial part of procedures. But Robotic surgeries powered by AI are increasing precision in the operating room. These systems assist surgeons in performing complex procedures with enhanced accuracy, reducing recovery times and improving surgical outcomes. Companies like Modmed are seriously working on the surgical procedures with the help of artificial intelligence.
6. Streamlining Healthcare Administration
AI is optimizing administrative tasks within healthcare systems, from scheduling appointments to managing patient records. This efficiency allows healthcare providers to focus more on patient care, improving overall service delivery.
7. Remote Monitoring and Telemedicine
AI-powered wearable devices and telemedicine platforms are facilitating continuous health monitoring, especially beneficial in remote or underserved areas. These technologies enable early detection of health issues and timely medical interventions.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
In my experience, many research projects that integrate biomedicine with AI are halted due to ethical guidelines, procedural requirements, and ethics approvals. While the promises of AI in Biomedicine are exciting, they come with these unavoidable challenges. Ensuring data privacy and addressing biases in AI algorithms are ongoing concerns in the scientific community. Ethical development and deployment of AI in healthcare are paramount to maintaining patient trust and upholding medical ethics.
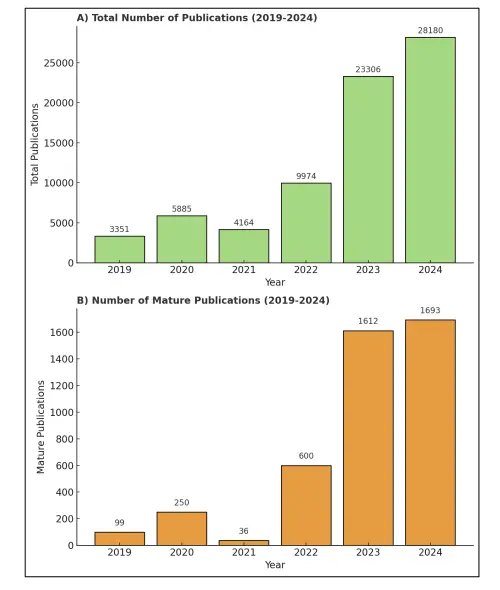
The analysis Ethical Challenges of Artificial Intelligence in Medicine done by Boudi et. al. (The above chart: Trends in AI in Healthcare Publications) shows the total number of AI-related biomedical publications each year from 2019 to 2024, illustrating an exponential rise in research activity (from ~3.3K in 2019 to ~28.2K in 2024). This surge underscores AI’s growing impact on medicine, but also highlights why robust oversight is needed. AI promises improved diagnostics and drug discovery, yet experts warn it brings “significant ethical challenges,” including transparency, bias, data privacy, and workforce.
Boudi, Ava L., Max Boudi, Connie Chan, F. Brian Boudi, and Ava Boudi. “Ethical Challenges of Artificial Intelligence in Medicine.” Cureus 16, no. 11 (2024).
Top Ethical Challenges and Risks of Using AI in Biomedicine (2025 Guide)
AI-related biomedical research has exploded, growing from 3,300 publications in 2019 to over 28,000 in 2024 (medrxiv.org). But alongside this surge, experts warn about serious ethical challenges.
Here are the top challenges facing AI in biomedicine today:
Discover the major ethical concerns and risks of using AI in healthcare, including data privacy, algorithmic bias, accountability, and patient autonomy. Learn with real-world examples and expert insights.
1. Data Privacy and Security
AI systems require vast amounts of sensitive patient data—medical records, genomic data, and health histories. This opens the door to data breaches.
Why it matters: AI centralizes patient data, making it a lucrative target for hackers.
Example: In 2024, Change Healthcare, a major U.S. health data processor, was hacked, exposing data from nearly 100 million patients, including names, Social Security numbers, and diagnoses (securityaffairs.com).
Impact: These breaches can lead to identity theft, loss of trust, and legal consequences. Even so-called “anonymized” genomic databases can be reverse-engineered, putting patient identities at risk.
2. Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
AI models learn from historical data, but if that data is biased, the AI can perpetuate discrimination.
Why it matters: Healthcare datasets often underrepresent minorities and vulnerable groups.
Example: An AI tool designed for high-risk patient care under-identified Black patients, because it used healthcare spending (historically lower for Black populations) as a proxy for risk (pewtrusts.org).
Impact: Biased AI can cause missed diagnoses, incorrect treatments, and worsen health disparities.
3. Lack of Explainability (Black Box AI)
Many AI tools—especially deep learning models—are difficult to interpret. Doctors and patients can’t always tell why an AI made a certain prediction.
Why it matters: In critical healthcare situations, understanding AI reasoning is essential for trust and safety.
Example: Tools like SHAP and LIME are being used to explain AI decisions in medical imaging. However, not all developers disclose how their models work, making transparency a challenge.
Impact: Lack of clarity can lead to errors, legal complications, and loss of clinical trust.
4. Accountability and Legal Liability
If an AI system causes harm, who is responsible? The doctor, the hospital, or the software developer?
Why it matters: Current legal systems were built around human decision-making, not autonomous algorithms.
Example: Courts are still debating how to handle AI-driven malpractice. In some cases, clinicians may be liable for following or ignoring AI advice, while developers might face lawsuits under product liability laws.
Impact: This legal gray area could discourage AI adoption or unfairly penalize professionals.
5. Regulatory Challenges
AI doesn’t fit neatly into traditional medical device regulations. Some AI tools update themselves continuously, making them hard to monitor.
Why it matters: Unlike drugs or fixed medical devices, AI systems can evolve after deployment.
Example: By 2025, the FDA had approved around 1,000 AI-enabled medical tools. However, many more remain in a gray area without clear oversight or informed consent rules (pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).
Impact: Until regulations catch up, hospitals and developers must navigate a confusing landscape of approvals, especially for AI tools with global reach.
6. Informed Consent and Patient Autonomy
Do patients have the right to know if an AI is involved in their treatment?
Why it matters: Patients may want to know how their diagnosis was made—whether by a human, AI, or both.
Example: A survey showed that many patients value knowing if AI assisted their care, sometimes as much as knowing drug side effects (pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).
Impact: Lack of transparency can undermine patient trust. Ethically, experts recommend that AI involvement be disclosed during the consent process.
7. Model Validation and Safety
AI models must be tested rigorously to avoid failures in real-world settings.
Why it matters: Many models work well in the lab, but fail in diverse clinical environments due to data drift or overfitting.
Example: The FDA now emphasizes “lifecycle management” for AI tools—meaning performance should be monitored after deployment, not just before approval.
Impact: Without continuous validation, AI may make dangerous errors that go undetected until harm occurs.
8. Workforce and Professional Implications
AI will reshape the roles of healthcare workers. While it can reduce workloads, it also threatens certain jobs.
Why it matters: Fields like radiology and pathology may see routine tasks automated, while demand for AI specialists grows.
Example: Studies show mixed feelings among professionals. Many believe AI will augment, not replace, their work, but they also fear job loss or skill redundancy.
Impact: Medical institutions must invest in upskilling and training programs to prepare staff for an AI-assisted future.
As AI transforms biomedicine, it brings both hope and serious ethical risks. From data privacy to algorithmic bias, and from explainability to legal responsibility, these challenges require ongoing attention.
What’s Needed:
- Clear regulations
- Transparent development
- Diverse training data
- Multidisciplinary collaboration
By addressing these concerns proactively, we can harness the full potential of AI in healthcare—safely and ethically
Future Directions
The future of AI in biomedicine is brimming with possibilities. Researchers are continually pushing boundaries, and breakthroughs are on the horizon. Keep an eye on this space for developments that could redefine healthcare.
In conclusion, AI is not just a buzzword; it’s a transformative force in biomedicine. From early disease diagnosis to personalized treatments and improved medical imaging, AI is reshaping healthcare. However, it’s essential to navigate this journey with care, addressing ethical concerns and ensuring that the benefits reach all corners of society.
Stay tuned for more updates on the incredible journey of AI in biomedicine. The future of healthcare is AI-driven, and the possibilities are limitless.
For Daily Updates, Connect With iLovePhD WhatsApp Channel

